As an Ontario personal injury lawyer with expertise in brain injury, I have helped many clients with injuries that were initially diagnosed as whiplash, but turned out to involve brain injury as well. That is why it is essential to always think ‘Brain First’. Unfortunately, these whiplash and brain injury victims can have trouble receiving the compensation they deserve and the treatment they need for their brain injuries.
What Is a Whiplash Injury and How Is It Related to Brain Injuries?
A whiplash injury can occur when a person’s head and neck move forward and backward in a sudden motion. This rapid movement can strain, stretch, or tear muscles and tendons in the neck, causing injury.
Whiplash is often associated with brain injury because when the head moves rapidly back and forth, the brain shifts inside the skull, hitting the front and back of the cranium. This is known as a coup-contrecoup injury, and can cause mild to moderate traumatic brain injuries.
The below video is a brief animation of what happens inside the head when a whiplash motion occurs:
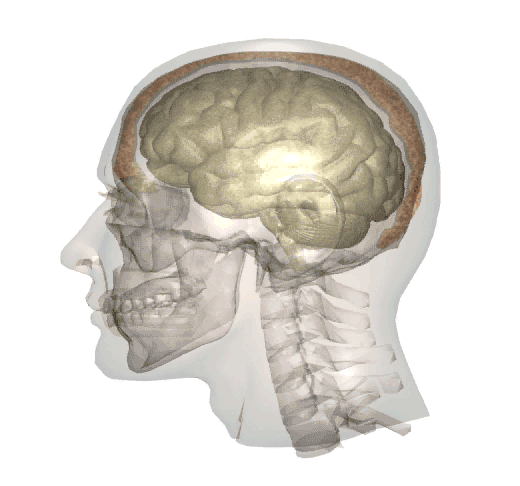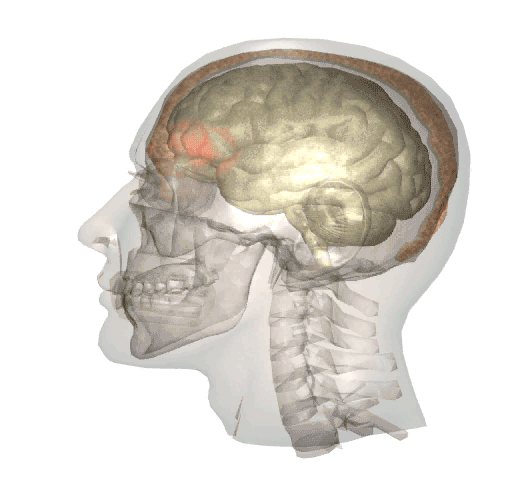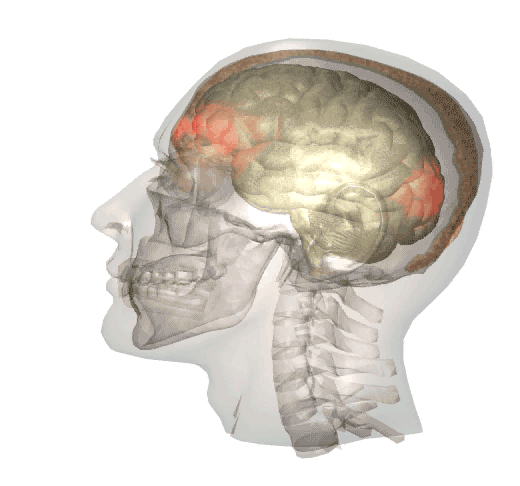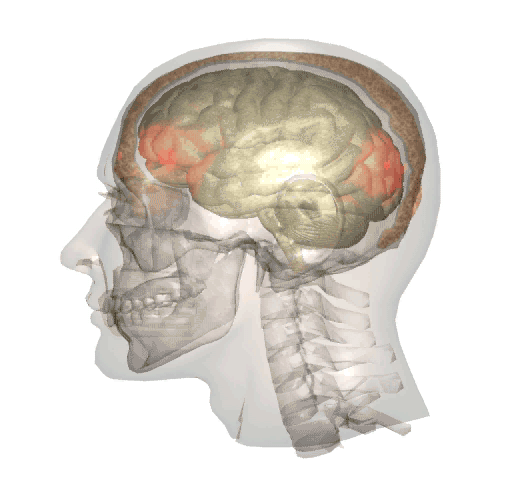
Whiplash injuries, and the possible brain injuries associated with them, are with the exception of sports injuries, most commonly caused by:
How Whiplash Injuries Are Classified
Whiplash injuries in Canada are graded into four categories of “Whiplash Associated Disorders” (WAD):
WAD I
WAD I is the most minor classification. It involves neck stiffness and tenderness.
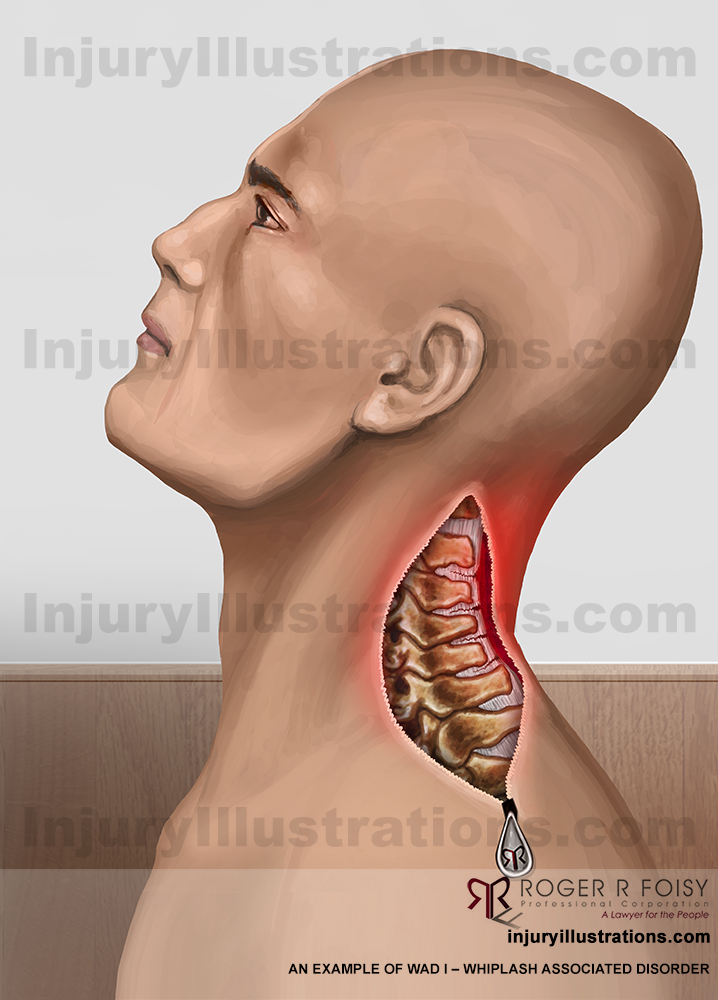
Whiplash Associated Disorder I
WAD II
WAD II is also considered to be minor. It involves WAD I symptoms along with musculoskeletal symptoms like decreased range of motion and point tenderness.
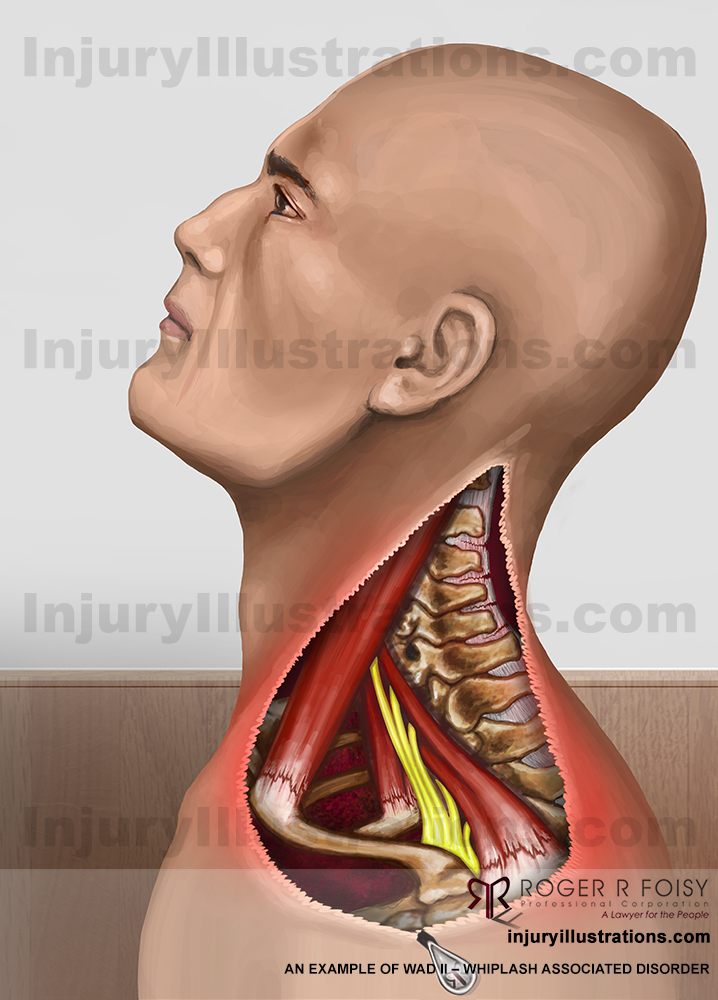
Whiplash Associated Disorder II
WAD III
WAD III is a more serious whiplash injury, involving WAD II symptoms along with neurological symptoms like decreased or absent deep tendon reflexes, sensory deficits, and weakness.
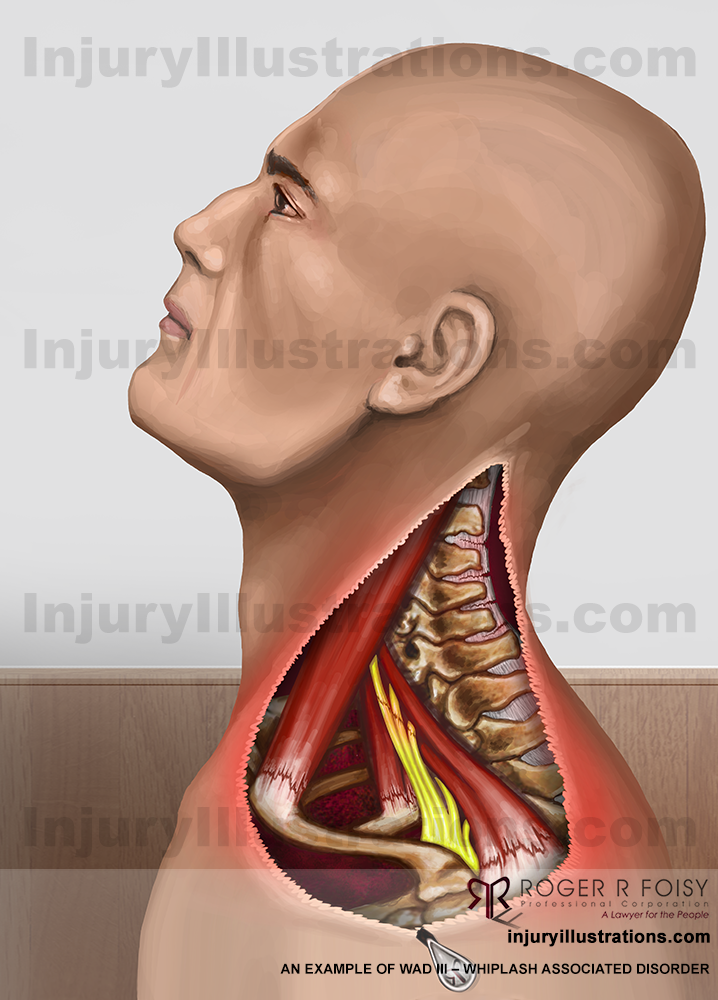
Whiplash Associated Disorder III
WAD IV
WAD IV is the most severe, involving an actual fracture or dislocation of the neck.
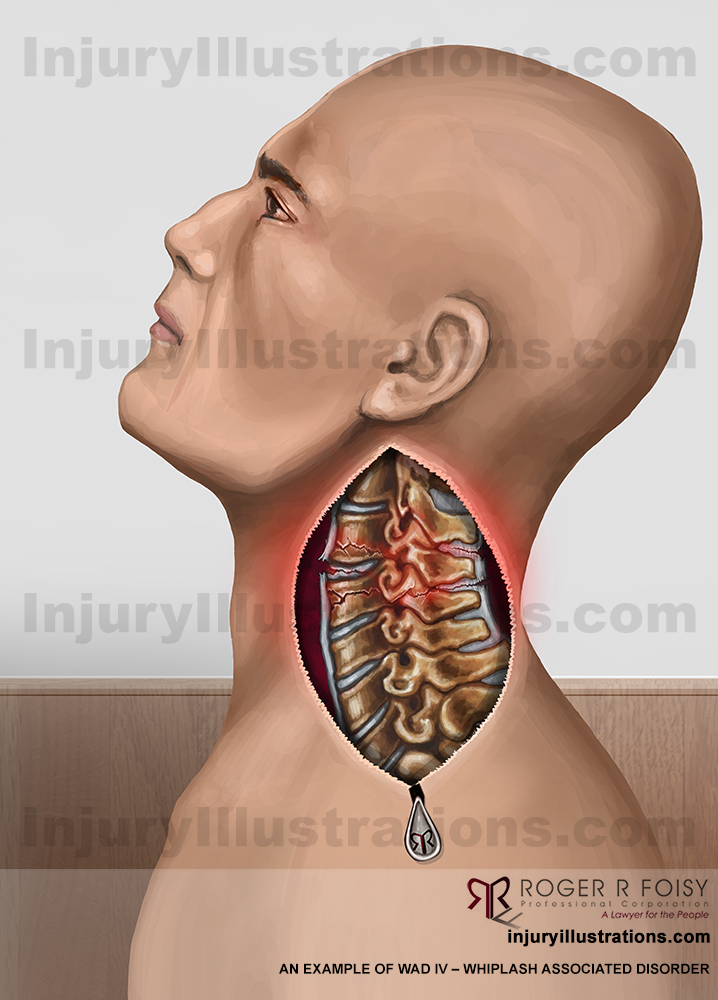
Whiplash Associated Disorder IV
In my experience, brain injuries tend to occur in WAD II cases and above; of course, it is possible for them to occur in WAD I injuries as well.
Unfortunately, WAD II is classified as “minor”. This has serious implications for compensation in Ontario automobile accidents through the Minor Injury Guideline (MIG). I highly recommend watching my previous video for a full discussion of this subject, “Accessing Funding for Medical Rehabilitation after Suffering a Mild Traumatic Brain Injury in a Motor Vehicle Accident”.
Essentially, motor vehicle accident (MVA) victims under the MIG can face compensation limitations. This is a serious problem in cases that turn out to involve brain injury.
However, all whiplash victims (not just MVA victims) can have trouble receiving the proper compensation for their brain injuries.
Why Victims, Healthcare Practitioners, and Lawyers Must Think ‘Brain First’ in Whiplash Injury Cases
In too many cases, brain injury symptoms are attributed to the whiplash injury, or any other physical injuries sustained in the accident (e.g. shoulder strain, broken arm, etc.).
When this happens, the victim encounters a host of challenges:
Incorrect Treatment that Can Make the Brain Injury Worse
If brain injury is present – but not diagnosed – in a whiplash injury, some of the treatments for whiplash can unintentionally aggravate the brain injury.
For example, neck maneuvering and manipulation therapies should be avoided in brain injury or concussion cases; however, they are a key treatment for whiplash. These kinds of movements can prolong the brain injury because they don’t give it the necessary time to heal on its own.
Furthermore, some medications should not be taken when a concussion/brain injury is involved.
In my personal opinion, head injury should always be ruled out before whiplash treatment begins to avoid making the injuries worse.
Delayed Diagnosis of Brain Injury
A WAD I or WAD II injury will typically resolve within 4 to 12 weeks. WAD III and WAD IV have lengthier recovery periods, depending on the specifics of the injury.
Too often, brain injury is only suspected after the person’s neck is healed and they are still experiencing headaches, ringing in the ears, or other neurocognitive symptomology. That means 4 to 12 weeks, or more, has passed without proper diagnosis of a brain injury that was present from the beginning but overlooked to the more obvious whiplash injury.
Difficulty Receiving Proper Compensation
If a brain injury is not diagnosed initially, it can be difficult to receive compensation.
In MVAs, the insurance company will ask why it was not included in the first medical reports and may dispute causation by suggesting a later incident caused the brain injury.
In court cases, it is more difficult for the lawyer to fight for compensation for a brain injury that wasn’t recorded by medical practitioners early on. The lawyer must gather evidence that the symptoms were present from the beginning, but were simply not recognized and diagnosed. This may be viewed as less credible than an early healthcare practitioner’s diagnosis of brain injury.
Knowing the Symptoms of Brain Injury Can Help You Tell the Difference
I believe everyone should know the symptoms of a brain injury, so they are able to get the correct diagnosis for themselves or a loved one.
A brain injury affects each person differently depending on the extent of the injury, the areas of the brain involved, and the individual person. Some possible symptoms include, but are not limited to:
- Physical: headaches, ringing in the ear, dizziness, insomnia, fatigue, trouble with senses, trouble with muscle coordination
- Cognitive: problems with attention, concentration, memory, information processing, reasoning, planning
- Emotional: irritability, depression, anxiety, mood swings, anger
Recognizing traumatic brain injury (including mild traumatic brain injury and concussions) is the first step to a proper diagnosis, receiving the treatment you need, and achieving the settlement you deserve.
Roger R. Foisy is an experienced Personal Injury Lawyer in Ontario who has helped clients with whiplash and brain injuries receive compensation. If you or a loved one has suffered a brain injury, please contact us for immediate support and a free consultation.
*Roger R. Foisy has completed courses in Neurorehabilitation, Advanced Brain Injury Rehabilitation, and Neuropsychological Assessments: Beyond Testing from Brock University. However, he is not a medical professional. The advice in this blog is not intended as a substitute for medical advice.
Watch My Mild Traumatic Brain Injury Video Series
More on Brain Injury from Roger R. Foisy:

